|
by Mitch Battros from EarthChangesMedia Website
The latest data continues to show
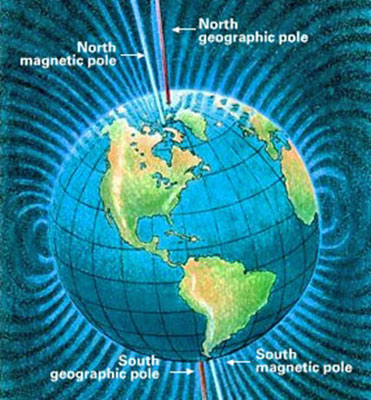
Earth’s magnetic field is weakening.
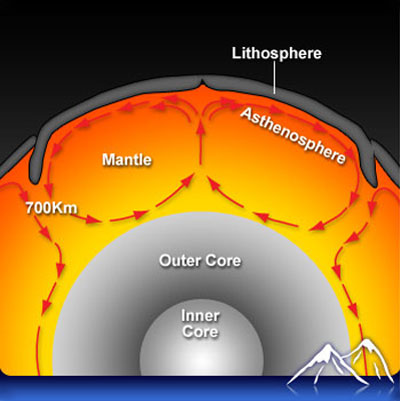
New research illustrates the shifting of magnetic flux, via Earth’s magnetic field - has a direct and symbiotic relationship to Earth’s,
This will continue until it reaches zero point, at which time there will be a full magnetic reversal.
Until this time, we will witness
magnetic north bouncing in the northern hemisphere. Closer to
the moments of a full reversal, we will see magnetic north drop down
below the equator.
Evidence for such events has been found
in sediment cores taken from deep ocean floors revealing magnetic
polarity shifts and its effect on Earth’s core.
As lava solidifies, it creates a record
of the orientation of past magnetic fields much like that of tree
rings.
In their samples, they found an excess of beryllium-10 (10Be), an isotope produced by cosmic rays and atoms of nitrogen and oxygen.
In sedimentary beds dating from the age
of the
Laschamp excursion, the researchers
found up to twice as much 10Be as normal, evidence of the intense
cosmic ray bombardment that the Earth underwent.
It is now moving faster at more than 40 miles per year since around 2001. This current trend of a weakening magnetic field suggests that Earth might undergo an excursion similar to the one that took place 41,000 years ago.
Since high energy cosmic rays has an effect on Earth’s core and can cause cell damage, such an event would have a significant impact on biodiversity, and in particular on humans.
This is why researchers are seeking to
find out a more accurate prediction of future magnetic field
excursions and reversals.
|