|
from
UniverseToday Website
as imaged by the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter.
Credit: HiRISE/MRO/LPL
(U. Arizona)/NASA
But among the rocky planets that make up
the inner Solar System, having moons is a privilege enjoyed only by
two planets: Earth and Mars. And for these two planets, it is a
rather limited privilege compared to gas giants like Jupiter and
Saturn which each have dozens of moons.
And whereas the vast majority of moons
in our Solar System are large enough to become round spheres similar
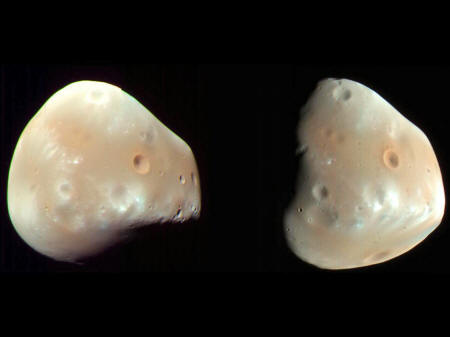
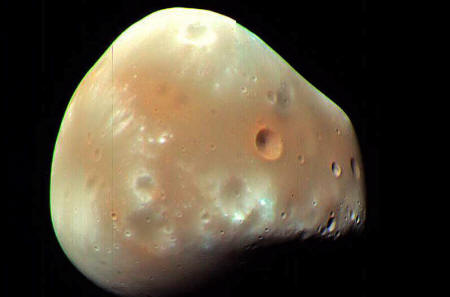
to our own Moon, Phobos and Deimos are asteroid-sized and misshapen
in appearance.
Phobos measures just 22.7 km across and
has an orbit that places it closer to Mars than Deimos. Compared to
Earth's own Moon - which orbits at a distance of 384,403 km away
from our planet - Phobos orbits at an average distance of only 9,377
km above Mars.
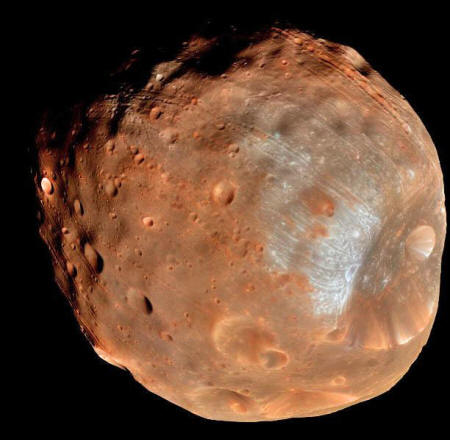
Phobos is heavily cratered from eons worth of impacts from meteors with three large craters dominating the surface.
The largest crater is Stickney (visible
in the photo below).
with the Stickney crater seen on the right side.
Credit: HiRISE, MRO,
LPL (U. Arizona), NASA
The crater is so large that scientists
believe the impact came close to breaking the moon apart. Parallel
grooves and striations leading away from the crater indicate that
fractures were likely formed as a result of the impact.
It is even smaller, measuring just 12.6
km across, and is also less irregular in shape. Its orbit places it
much farther away from Mars, at a distance of 23,460 km, which means
that Deimos takes 30.35 hours to complete an orbit around Mars.
As the moon revolves, the debris is
redeposited as a dusty layer on its surface.
Credit: HiRISE/MRO/LPL
(U. Arizona)/NASA
Both are lumpy, heavily-cratered and
covered in dust and loose rocks. They are among the darker objects
in the solar system. The moons appear to be made of carbon-rich rock
mixed with ice. Given their composition, size and shape, astronomers
think that both of Mars' moons were once asteroids that were
captured in the distant past.
This family of asteroids is extremely
old, dating back to the formation of the Solar System. Hence, it is
likely that they were acquired by Mars very early in its history.
However, it appears that of these two satellites, Phobos won't be
orbiting the Red Planet for very much longer.
And then a few million years later,
those rocks will crash down on the surface of Mars in a spectacular
string of impacts.
Ninety-four years after the moons' discovery, NASA's Mariner 9 spacecraft got a much better look at the two moons from its orbit around Mars. Upon viewing the large crater on Phobos, NASA decided to name it after Hall's wife - Stickney.
Subsequent observations conducted by the
HiRISE experiment, the
Mars Global Surveyor, and the
Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter have
added to our overall understanding of these two satellites.
|