|

by Linda Moulton Howe
2008
from
EarthFiles Website
“Smith's Cloud is eleven thousand
light-years long, 2,500 light-years wide and is only 8,000
light-years from our Milky Way Galaxy's disk. It is moving
toward out galaxy at more than 150 miles per second, aimed
to strike at an angle of about 45 degrees.”
- National Radio Astronomy
Observatory

The Very Large
Array (VLA) near Socorro, New Mexico.
Image courtesy NRAO/Laure
Wilson Neish.
January 12 , 2008 Austin, Texas
-
The National Radio Astronomy Observatory (NRAO) is a
facility of the National Science Foundation, operated under
cooperative agreement by Associated Universities, Inc.
Its headquarters and technology center
are in Charlottesville, Virginia which coordinate the research of
the Green Bank Telescope (GBT) in West Virginia; the
Very Large Array, Very Long Baseline Array and Expanded Very Large
Array in Socorro, New Mexico; and two other instruments in Tucson,
Arizona, and Santiago, Chile.
On Friday, January 11, 2008, NRAO released the following report at
the American Astronomical Society meeting in Austin, Texas:
“A giant cloud of hydrogen gas is
speeding toward a collision with our Milky Way Galaxy, and when
it hits - in less than 40 million years - it may set off a
spectacular burst of stellar fireworks.
‘The leading edge of this cloud is
already interacting with gas from our Galaxy,’ said Felix J.
Lockman, of the National Radio Astronomy Observatory
(NRAO), leader of a team of astronomers who used the
National Science Foundation's Robert C. Byrd Green
Bank Telescope (GBT) to study the object.
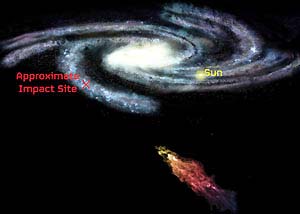
NRAO Illustration of
Smith Cloud Approaching Milky Way Galaxy
Artist's
conception of Smith's Cloud approaching, then colliding with,
our own Milky Way Galaxy in approximately 40 million years, a
long way from
our yellow sun.
Credit: Bill Saxton, NRAO/AUI/NSF.

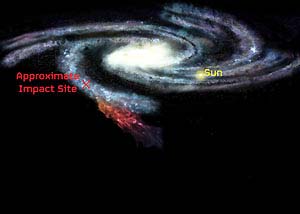
Actual image by Green Bank Telescope of Smith's Cloud,
which is headed toward a collision with the Milky Way.
Image credit:
Bill Saxton, NRAO/AUI/NSF.
The scientists presented their findings
to the American Astronomical Society's meeting in Austin, Texas.
The cloud, called Smith's Cloud, after the astronomer who
discovered it in 1963, contains enough hydrogen to make a million
stars like the Sun.

Smith's Cloud
Smith's Cloud is eleven thousand
light-years long, 2,500 light-years wide and is only 8,000
light-years from our Milky Way Galaxy's disk.
It is moving toward out galaxy at more
than 150 miles per second, aimed to strike at an angle of about 45
degrees.
‘This is most likely a gas cloud
left over from the formation of the Milky Way or gas stripped
from a neighbor galaxy. When it hits, it could set off a
tremendous burst of star formation. Many of those stars will be
very massive, rushing through their lives quickly and exploding
as supernovae. Over a few million years, it'll look like a
celestial New Year's celebration, with huge firecrackers going
off in that region of the Galaxy,’ Lockman said.
When Smith's Cloud was first
discovered, and for decades after, the available images did not have
enough detail to show whether the cloud was part of the Milky Way,
something being blown out of the Milky Way, or something falling in.
Lockman and his colleagues used the Green Bank Telescope
to make an extremely detailed study of hydrogen in Smith's Cloud.
Their observations included nearly 40,000 individual pointings of
the giant telescope to cover the cloud with unprecedented
sensitivity and resolution.
Smith's Cloud is about 15 degrees
long in the sky, 30 times the width of the full moon.
‘If you could see this cloud with
your eyes, it would be a very impressive sight in the night
sky,’ Lockman said. ‘From tip to tail it would cover almost as
much sky as the Orion constellation. But as far as we know it is
made entirely of gas - no one has found a single star in it.’
The detailed GBT (Green Bank
Telescope) study dramatically changed the astronomers’
understanding of the cloud. Its velocity shows that it is falling
into the Milky Way, not leaving it, and the new data show that it is
plowing up Milky Way gas before it as it falls.
‘Its shape, somewhat similar to that
of a comet, indicates that it's already hitting gas in our
Galaxy's outskirts,’ Lockman said. ‘It is also feeling a
tidal force from the gravity of the Milky Way and may be in the
process of being torn apart. Our Galaxy will get a rain of gas
from this cloud, and then in about 20 to 40 million years, the
cloud’s core will smash into the Milky Way’s plane,” Lockman
explained.
Smith's Cloud will likely
strike a region somewhat farther from the Galactic center than
our Solar System and about 90 degrees ahead of us in the Milky
Way disk. The collision may trigger a period of rapid star
formation fueled by the new gas and the shock from the
collision. Some theories say that the ring of bright stars not
far from our own Sun, called
Gould's Belt, was created by
just such a collision event.”
[See Gould's Belt Survey.]
|