|
from
BigThink Website
NASA/JPL-Caltech.
Some physicists say its subatomic particles. Others believe its energy or even space-time. One of the more radical theories suggests that information is the most basic element of the cosmos.
Although
this line of thinking emanates from the mid-20th century, it seems
to be enjoying a bit of a Renaissance among a sliver of prominent
scientists today. Consider that if we knew the exact composition of the universe and all of its properties and had enough energy and know-how to draw upon, theoretically, we could break the universe down into ones and zeroes and using that information, reconstruct it from the bottom up.
It's the information, purveyors
of this view say, locked inside any singular component that allows us to manipulate matter any way we choose. Of course, it would take deity-level sophistication, a feat only achievable by a type V civilization on the Kardashev scale.
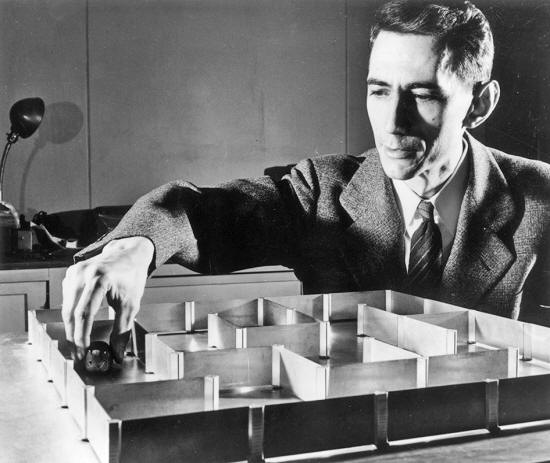
Mid-20th century mathematician and engineer Claude Elwood Shannon, is thought the creator of classical information theory.
Though few know of him outside of scientific circles, he's being hailed today as the "father of the digital age."
Shannon's spark of genius came in 1940 at MIT, when he noticed a relationship between Boolean algebra and telephone switching circuits.
Claude E. Shannon with his electronic mouse. Bell Labs, 1952. Getty Images.
Soon after, he was hired by Bell Labs to devise the most efficient way to transfer information over wires.
In 1948, he penned "A Mathematical Theory of Communication," essentially laying the foundation for the digital age. Shannon was the first to show that mathematics could be used to design electrical systems and circuits.
Before him, it was done through expensive model-making, or mere trial and error. Today, Boolean algebra is used to design communication and computer systems, hardware, software, and so much more.
Basically, anything that generates, stores, or transfers information electronically, is based on Shannon's tome.
That's not all. Shannon defined a unit of information, the binary unit or bit. Bits are a series of 0s and 1s, which help us to store and recall information electronically.
Moreover, he was the first to transform data into a commodity. Its value he said was proportional to how much it surprised the consumer.
In addition, he connected electronic communication to thermodynamics. What's now called "Shannon entropy," measures the disorder or randomness inherent in any communications system.
The greater the entropy, the less clear the message, until it becomes unintelligible.
As for information theory, he developed that during World War II, while trying to solve the problem of sending an encrypted message over a static-ridden telephone or telegraph line.
Claude E. Shannon laid the groundwork for communication technology. Getty Images.
To look at information theory from a quantum viewpoint, the positions of particles, their movement, how they behave, and all of their properties, give us information about them and the physical forces behind them.
Every aspect of a particle can be expressed as information, and put into binary code.
And so subatomic particles may be the bits that the universe is processing, as a giant supercomputer. Besides quantum mechanics, since Shannon elucidated it, information theory has been applied to music, genetics, investment, and much more.
Science writer James Gleick, author of The Information, contends that it wasn't Shannon, but early 19th century mathematician Charles Babbage, who first called information the central component of all and everything.
Babbage is credited for first conceptualizing the computer, way before anyone had the ability to even build one.
The eminent John Archibald Wheeler in his later years was a strong proponent of information theory.
Another unsung paragon of science, Wheeler,
Physicist John Wheeler coined the term black hole. By Deutsch: Ute Kraus, Wikimedia Commons.
Wheeler said the universe had three parts:
In the 1980s, he began exploring possible connections between information theory and quantum mechanics.
It was during this period he coined the phrase "It from bit."
The idea is that the universe emanates from the information inherent within it. Each it or particle is a bit. It from bit.
In 1989, Wheeler produced a paper to the Santa Fe institute, where he announced,
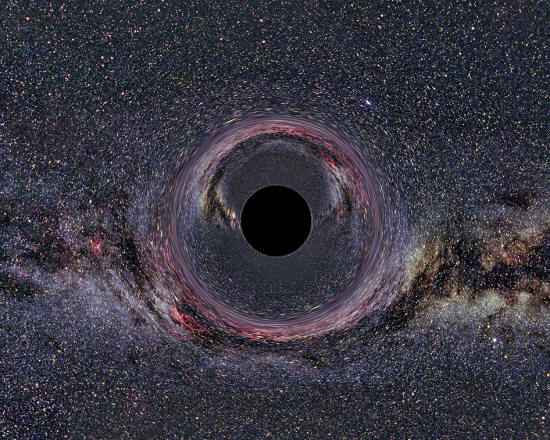
A team of physicists earlier this year announced research conclusions that would make Wheeler smile.
We might be caught inside a giant hologram they state. In this view, the cosmos is a projection, much like a 3D simulation. What's weird is that the laws of physics operate well in a 2D quantum field within a 3D gravitational one.
It's important to note that most physicists believe that matter is the essential unit of the universe. And information theory's proof is limited.
After all, how would you test for it?
Is the universe a giant hologram inside a supercomputer? Getty Images.
If the nature of reality is in fact reducible to information itself, that implies a conscious mind on the receiving end, to interpret and comprehend it.
Wheeler himself believed in a participatory universe, where consciousness holds a central role.
Some scientists argue that the cosmos seems to have specific properties which allow it to create and sustain life. Perhaps what it desires most is an audience captivated in awe as it whirls in prodigious splendor.
Modern physics has hit a wall in a number of areas. Some proponents of information theory believe embracing it may help us to say, sew up the rift between general relativity and quantum mechanics.
Or perhaps it'll aid in detecting and comprehending dark matter and dark energy, which combined are thought to make up 95% of the known universe. As it stands, we have no idea what they are. Ironically, some hard data is required in order to elevate information theory.
Until then, it remains theoretical.
To learn more about information theory as the basis of the universe, watch below video:
|