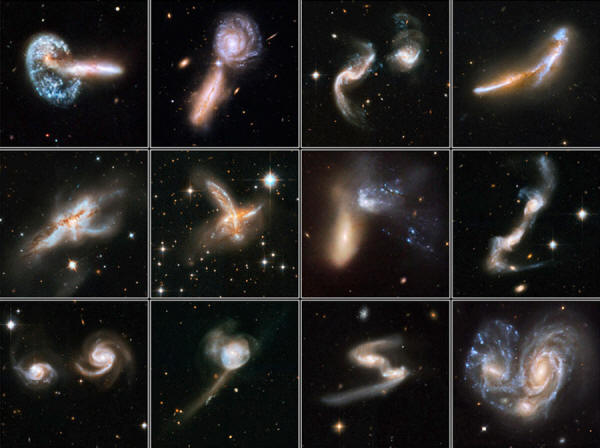
|
by Stephanie Pappas
With numbers that large, you can bet that there are some real weirdoes out there. Out beyond our Milky Way, there are,
Here are some of the strangest galaxies out there.
The galaxy is a barred spiral galaxy - together, its stars form a spiral shape with a bar-shaped center - with a twist:
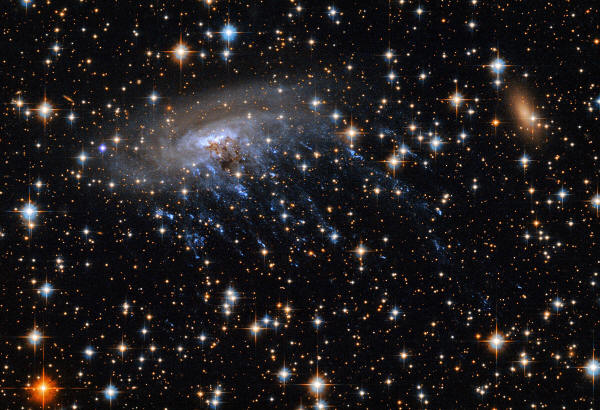
According to NASA, these stars are forming inside a tail of dust and
gas (invisible to the naked eye) that streams off ESO 137-001. This
formation process is a bit of a mystery, as the gases in the tail
should be too hot for star formation.
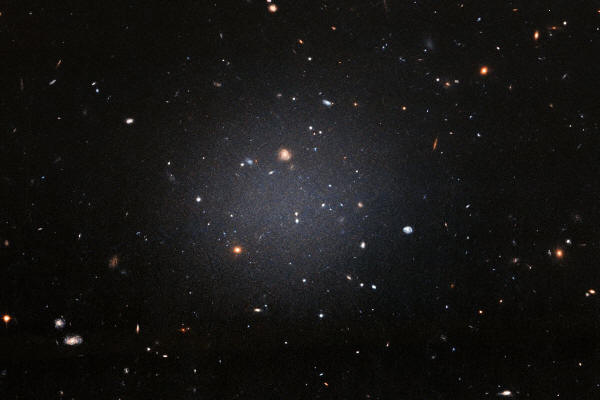
This discovery immediately raised red flags.
Dark matter is a
mysterious form of matter that interacts with gravity, but not with
light. It makes up more of the total matter in the universe than the
matter we can see, so finding a galaxy without any was bizarre, to
say the least.
That change in distance completely alters the calculations for the galaxy's mass. Turns out, it's a pretty normal galaxy after all, and the universe (kind of) makes sense again.
what the young, ‘dead,' disk galaxy MACS2129-1 (right)
would
look like.
The discovery of this galaxy was a head-scratcher. Scientists believed that galaxies of this sort had formed by merging with smaller galaxies over time, but MACS2129-1's stars didn't form from these sort of explosive mergers; they formed early on, in the disk of the original galaxy.
The findings (A Massive, Dead Disk Galaxy in the Early Universe), published in the journal Nature in 2017, suggest that dead galaxies somehow internally rearrange their structure as they age rather than changing shape because they combine with other galaxies.
shows the Andromeda galaxy, the Milky Way's closest neighbor at about 2.5 million light-years away,
glowing
in ultraviolet light.
The Andromeda galaxy, Earth's largest neighbor, has been devouring smaller galaxies for at least 10 billion years, according to 2019 research.
In another 4.5 billion years, the Andromeda galaxy and the Milky Way galaxy will collide, although it's not yet clear who will devour whom in that cosmic pile-up.
(Earthlings, unfortunately, will not be around to see this clash play out, as our own sun is heating up and will likely make life on Earth impossible between about 1 billion and 5 billion years from now.)
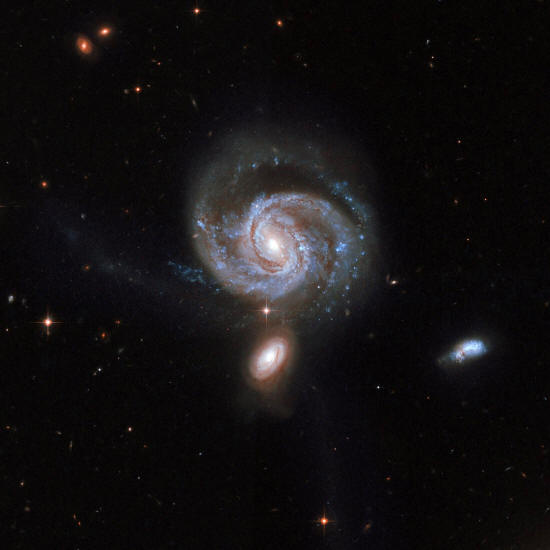
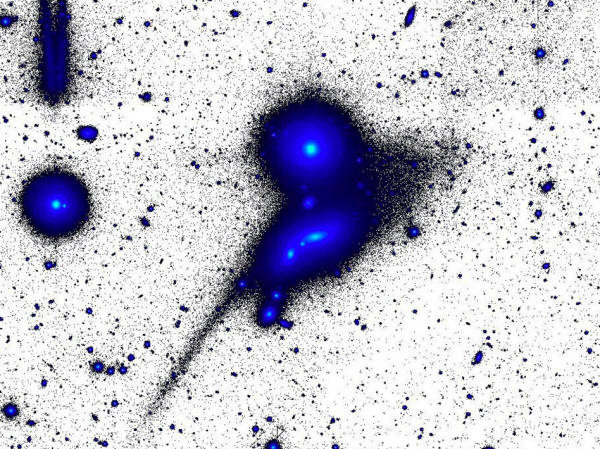
consists of the two "smudges"
at the
centre of the image.
A cosmic collision, researchers reported in 2018 in the journal Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. Two disk galaxies pulled on a smaller dwarf galaxy, clumping the stars on one end into a "head" and leaving the others to stream out in a long "tail."
This arrangement is for a limited time only, though. In a few billion years, the galaxies will merge together with some others in the vicinity to create one single galaxy.
the most luminous known galaxy,
and
three companion galaxies.
The brightest known
galaxy in the universe is one of these thieves. In 2018, scientists
announced that they'd observed the
galaxy W2246-0526 sucking up half
the mass
of three nearby galaxies.
The observation is the most distant direct snapshot of galactic cannibalism and the only known example of a galaxy siphoning off more than one neighbor at a time.
and Little Cub (right), a small, metal-poor galaxy
that
may be a companion of NGC 3359.
This dwarf galaxy has
been largely dormant since the Big Bang, which means that it might
contain molecules unchanged since just moments after the rapid
expansion of the universe 13.7 billion years ago.
Still, the opportunity to watch NGC 3359 strip the star-forming gases from Little Cub is valuable to science, because astronomers may be able to measure the signatures of those early-universe molecules before they're gone.
are captured here in a new image from the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope,
set
against a backdrop of distant galaxies.
This galaxy, 270 million
light-years from Earth, is in the constellation Centaurus. It's a
lenticular galaxy, a hybrid between a spiral galaxy like the Milky
Way and a stretched-out elliptical galaxy.
It's possible that the
blooms are shock waves from a relatively recent galactic collision
that also provided the galaxy with new fuel for star formation.
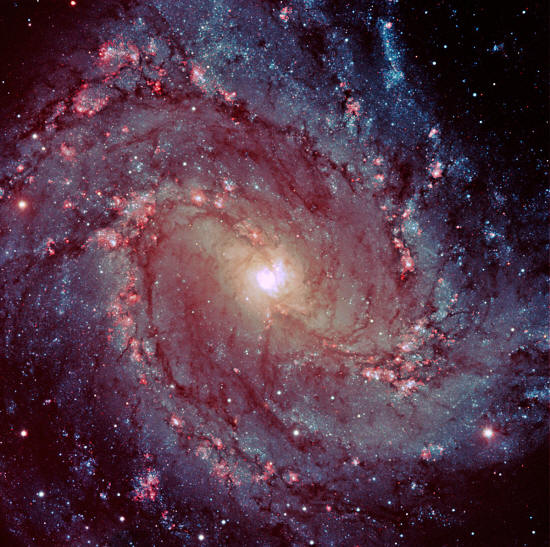
Pretty Pinwheel
also
called Messier-83.
Messier 83 is weird in a couple ways.
This puts Messier 83 in second place for supernovas, as only the galaxy NGC 6946 has produced more observable supernovas, with nine).
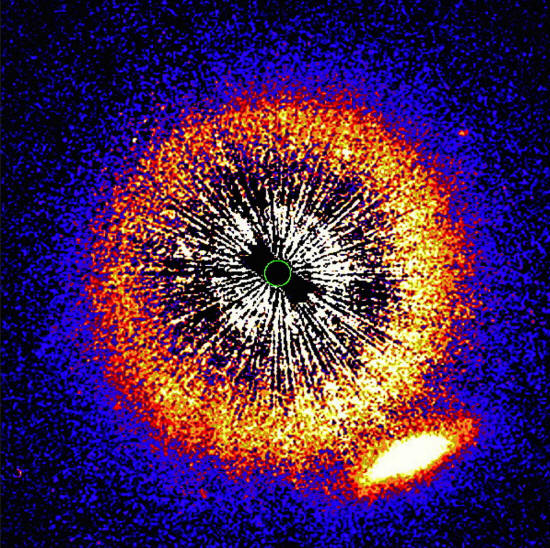
with and pass behind a star
sitting
nearer to us within the Milky Way.
The galaxy is nicknamed the Vermin galaxy by some scientists because its light gets in the way of studying the closer star and its system. In 2020, the star will fully obscure the galaxy.
Before then, scientists can study the spectra of light as the galaxy makes its transit behind the star, perhaps gleaning some information about the debris around the star from the light that makes its way through.
have distorted the shape of IC 2163, flinging out stars and gas into long streamers stretching out a hundred thousand light-years
toward
the right-hand edge of the image.
and The
Hubble Heritage Team (STScI))
The disk of spiral galaxy IC 2163 seems to peer out into space with an enormous eye. This eye-shaped feature is actually a huge stream of stars and dust, produced when IC 2163 (at right in image) brushed against another spiral galaxy, NGC 2207 (left).
These "ocular features" last only a few tens of millions of years, astronomer Michele Kaufman, who reported the discovery in 2016, said in a statement.
That's a blink of an eye
(pun intended) in the life span of a galaxy, so discovering one is a
unique opportunity.
The deceleration causes the gas to pile up and compress, which could set the stage for the formation of new stars.
is the brightest and largest member of the so-called Hickson 96 compact group of galaxies,
consisting of four galaxies. (STScI/AURA)-ESA/Hubble Collaboration
and A.
Evans (University of Virginia, Charlottesville/NRAO/Stony Brook
University))
A few, though, contain not one, but two black holes.
The only other galaxy known to have two black holes at its heart is a supermassive galaxy called 0402+379.
of
galaxy NGC 1277.
-
Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias)
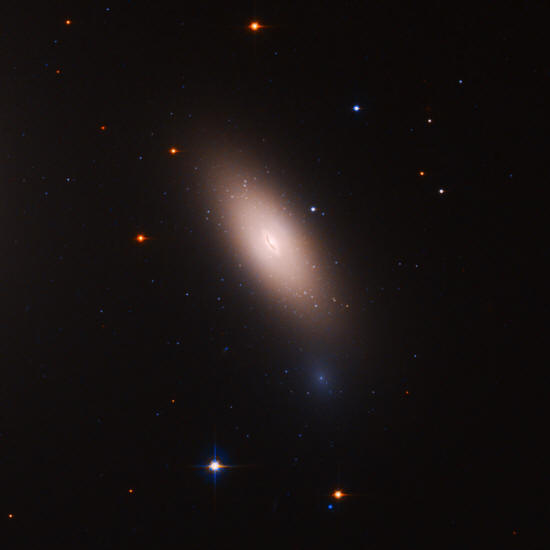
This galaxy,
first reported in 2018, is a mere 240 million
light-years from Earth. It hasn't formed new stars for about 10
billion years, making it a dead galaxy.
Without gas and dust from alien galaxies, NGC 1277 no longer forms stars.
Some astronomers think that most galaxies started out looking at lot like NGC 1277, evolving spiral and other shapes only through later mergers with one another.
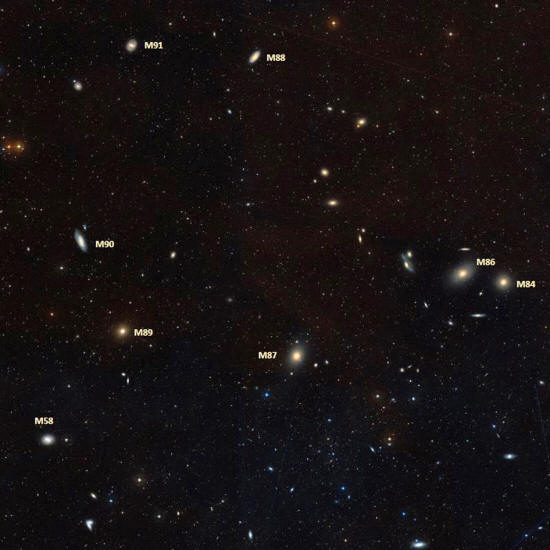
Objects moving away from Earth are redshifted, meaning their light emissions are weighted toward red. Messier 90 is part of a large group of galaxies called the Virgo Cluster.
It can be seen from the Northern Hemisphere in May with a telescope or binoculars, sitting between the constellations Virgo and Leo, according to NASA.
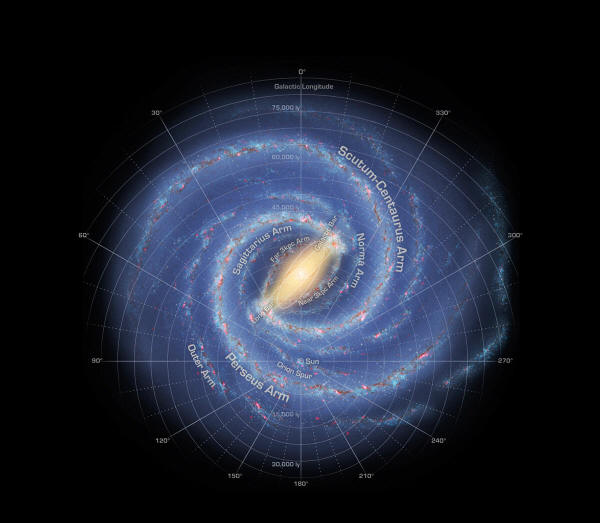
is organized into spiral arms of giant stars that illuminate interstellar gas and dust.
The sun
is in a finger called the Orion Spur.
Now, all six of these galaxies belong to the Milky Way's orbit.
As a bonus, the study also
found that the Large Magellanic Cloud is stranger than previously
believed. It hosts many tiny dwarf
galaxies, some of which are so faint that they don't even have
stars, only
dark matter.
|