|

2009, 2010 and 2014
from
WakingTimes,
Nature
and
YouTube Website

Keeping a sense of perspective in these crazy times is imperative,
and as astronomy pushes the envelope, seeking an ever greater
understanding of our place in the cosmos, we are sometimes rewarded
with fascinating new visual interpretations of our universe that
have the power to completely re-write our sense of purpose and
possibility.
Making the struggles we have here on Earth seem small.
The following 3 videos are inspiring examples of how technology can
assist in our evolution, and help us to keep stay grounded, by
providing us renewed perspectives on life here on Gaia.
Laniakea - The
Immeasurable Universe
2014
Thanks to the recent work of a team of researchers at the University
of Hawaii, we now have an even better of idea of just how tiny our
little lives are in the big picture of the universe.
In fact, as a
new model for mapping the movement of galaxies has revealed, the
cluster of galaxies that is home to planet earth may be around 100
times bigger than previously thought.
Setting out to answer the question, "where in the universe is the
Milky Way?," the team of scientists has drawn a compelling new map
of the super cluster of galaxies which is our home, in relation to
neighboring clusters.
Gathering data on the positions and relative
movements of over 8000 galaxies, while accounting for the effects of
the continuous tug of gravity, they have mapped the cosmic flows, or
flight paths of these galaxies, which gives the most comprehensive
picture we've ever had of how the universe organizes itself.
"Scientists previously placed the
Milky Way in the Virgo Supercluster, but under Tully and
colleagues' definition, this region becomes just an appendage of
the much larger Laniakea, which is 160 million parsecs (520
million light years) across and contains the mass of 100 million
billion Suns."
[below report from Nature]
Earth's new address - 'Solar System,
Milky Way, Laniakea'
by Elizabeth Gibney
03 September 2014
from
Nature Website
Analysis of galaxies
shows local supercluster
to be 100 times larger
than previously thought.
The supercluster of galaxies
that includes the Milky Way is 100 times bigger in volume
and mass than previously thought, a team of astronomers
says.
They have mapped the enormous region and given it the
name
Laniakea - Hawaiian for 'immeasurable heaven'.
Galaxies tend to huddle in groups called clusters; regions
where these clusters are densely packed are known as
superclusters.
But the definition of these massive cosmic
structures is vague.
The new study, published in Nature,1 describes a novel way
to define where one supercluster ends and another begins.
A
team led by Brent Tully, an astronomer at the University of
Hawaii in Honolulu, charted the motions of galaxies to infer
the gravitational landscape of the local Universe, and
redraw its map.
Cosmic speed
The team used a database 2 that compiles the velocities of
8,000 galaxies, calculated after subtracting the average
rate of cosmic expansion.
"All these deviations are due to
the gravitational pull galaxies feel around them, which
comes from mass," says Tully.
The researchers used an
algorithm to translate these velocities into a
three-dimensional field of galaxy flow and density.
"We
really can't claim to have a good understanding of cosmology
if we cannot explain this motion," says Tully.
This method is superior to merely mapping the location of
matter, because it enables scientists to build a map of
uncharted regions of the Universe, says Paulo Lopes, an
astrophysicist at the Valongo Observatory, part of the
Federal University of Rio de Janeiro.
It relies on detecting
the galaxies' influence, rather than seeing them directly.
Moreover, the galaxies' motions reflect the distribution of
all matter, not just that which is visible in our telescopes
- including dark matter.
Discounting cosmic expansion, their map shows flow lines
down which galaxies creep under the effect of gravity in
their local region (see below video). Based on this, the
team defines the edge of a supercluster as the boundary at
which these flow lines diverge.
On one side of the line,
galaxies flow towards one gravitational centre; beyond it,
they flow towards another.
"It's like water dividing at
a watershed, where it flows either to the left or right
of a height of land," says Tully.
Frontiers in space
This is a completely new definition of a supercluster.
Scientists previously placed the Milky Way in the Virgo Supercluster, but under Tully and colleagues' definition,
this region becomes just an appendage of the much larger
Laniakea, which is 160 million parsecs (520 million light
years) across and contains the mass of 100 million billion
Suns.
However, this work is unlikely to be the final word on what
a supercluster is, says Gayoung Chon, an astronomer at the
Max Planck Institute for Extraterrestrial Physics in
Garching, Germany.
Her team works on a different definition,
based on superclusters being structures that will one day
collapse into a single object.
This will not happen to Laniakea,
she estimates, because some of the galaxies within it will
recede from one another forever.
"The definition you use
really depends on the questions you want to ask. This
latest method is a very good way to chart the
large-scale structures of the Universe, but it doesn't
ask what will happen to these superclusters eventually,"
she says.
Although the map is
comprehensive over the Universe around the Milky Way, its
distance measurements become less accurate, and less
numerous, the farther out you go, says Lopes.
This is currently the
technique's biggest potential source of error, he says, but
adding more galaxy measurements will improve the map and
could eventually help scientists to fully trace what is
behind the motion of our local group of galaxies.
References
-
Tully, R. B., Courtois, H.,
Hoffman, Y & Pomarède, D.
Nature 513, 71–73 (2014).
The new study, published in Nature1, describes a novel
way to define where one supercluster ends and another
begins…
-
Tully, R. B. et al. Astron.
J. 146 86 (2013).
The team used a database2 that compiles the velocities
of 8,000 galaxies, calculated after subtracting the
average rate of cosmic expansion…
Calling this newly defined section of
the universe, Laniakea, which means 'Immeasurable Heaven', the new
computer simulations give a mind-opening perspective on how small
our solar system truly is in the infinite cosmic web that makes up
the universe.
Furthermore, the similarities between
the designs that emerge in this new 3-dimensional map, and the
diagrams of how neural networks within the human brain are organized
reinforces the notion, 'as above, so below,' giving us visual
evidence of the inseparable connections between our outer and inner
worlds.
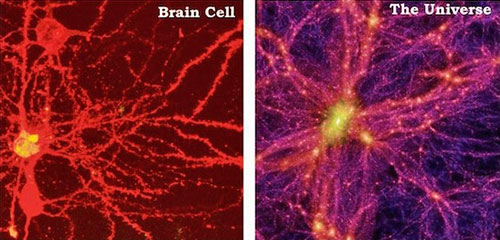
Take a look at this humbling new map of our corner of the universe:
Hubble The Most
Important Images Ever Taken
2010
The Hubble space telescope has changed the relationship that human
beings have with the heavens above, bringing us images that baffle
the mind, showing just how densely and infinitely packed the
universe is with other galaxies, solar systems, stars and planets.
Some have called the Hubble images the
most important photographs ever taken, because they give us a true
bit of perspective to the unfathomable size and scope of our
universe, while revealing the breath-taking celestial beauty that
comprises the heavens.
"Astronomers, 1996, attempted to do
something extraordinary. They pointed the Hubble Space Telescope
into a part of the sky that seemed utterly empty.
A patch devoid of any planets, stars
and galaxies. This area was close to the Big Dipper, a very
familiar constellation, and the path of sky was no bigger than a
grain of sand held out at arm's length…"
Here is what they found:
The Detailed
Universe
2009
The Detailed Universe takes you on a simulated journey from nano-meters
to billions of light years.
Beginning with planet earth, the video
zooms out from the planet to reveal the scale of our solar system,
our galaxy, then the surrounding galaxies that fill the void we call
space.
Zooming back into planet earth, the
picture of our inter-connectedness becomes clear as the camera dials
in on the planet, then furthermore, into to the biological
structures that make up life.
Beyond DNA lies the atomic structures
that resemble the cosmos surrounding the planet, suggesting that an
entire universe may ultimately be alive within each electrical
charge that makes up the human body.
"The nitrogen in our DNA, the
calcium in our teeth, the iron in our blood, the carbon in our
apple pies were made in the interiors of collapsing stars. We
are made of starstuff."
Carl Sagan, Cosmos
Watch this consciousness expanding video
now:
Our exploration of the universe around us
is one of the most
inspiring endeavors
of the human race,
and these 3 videos
have the
power to help us along
in our personal and collective evolution.
|



