|
Referencing the findings of a new paper published in Nature entitled "Persistent warm Mediterranean surface waters during the Roman period" along with his own research into solar activity, Higgs concludes here that the Sun overwhelmingly controls our climate.
According to Dr Higgs,
Yet CO2, the source of all life (photosynthesis), is still near its lowest level in 500 million years, only just above plant-starvation level.
Before our very eyes CO2 is beneficially greening our Earth and increasing crop production, giving hope for feeding our 8 billion (rapidly growing) human population.
Instead of celebrating we pathetically cringe,
concludes a bewildered Dr Higgs.
Conclusions of the new Scientific Study
"Persistent warm Mediterranean surface waters during the Roman period" by G. Margaritelli et al. 2020, reveals,
...this period of warmth is linked to prosperity and the empire's expansion (the "Roman Climatic Optimum"), while, conversely, prolonged periods of cold correlate with times of suffering, famine, and, ultimately, the collapse of the Roman Empire.
According to the paper, comparisons between their recently discovered record with previously published Mediterranean SST records from the Alboran Sea, Minorca Basin and Aegean Sea and northern Hemisphere temperature reconstructions,
The paper concludes that after the Roman Period, a general cooling trend developed in the region with several minor oscillations:
The new generated Mg/CaG. ruber SST (sea surface temperature) record from Sicily channel allows to identify a series of climate events that can be associated to different remarkable socio-cultural developments of ancient Mediterranean civilizations for the last five millennia.
Warm events are associated to historical periods such as the Cooper age, the Early and Late Bonze age while cold events are associated to the Homeric and Greek periods.
The comparison of this new SST record with previous published Mediterranean SST records from, ...highlight the overall perseverance of warm conditions during the Roman Period (1 CE to 500 CE).
These warm conditions were particularly intense in the Sicily record, that reflect summer months, and correspond to the so called "Roman Climatic Optimum".
During this period, in fact, developed the greatest ancient civilization of all time, the Roman one...
We hypothesize the relevance that these climate conditions may had in the expansion of the Roman Empire and its collapse with the general development of colder conditions...
A cooling trend dominated after the Roman period reaching minimum values, in the whole Mediterranean, by the end of the LIA, minor oscillations punctuated this cold trend and were also associated with socio-cultural changes in central Mediterranean region.
As we regularly conclude, periods of warmth/warming should be embraced and capitalized upon - it's those times of cold/cooling that we need to concern ourselves with.
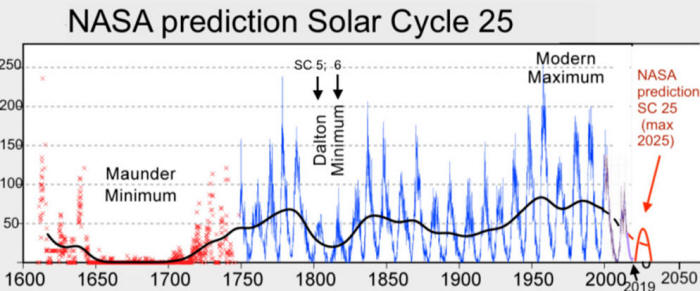
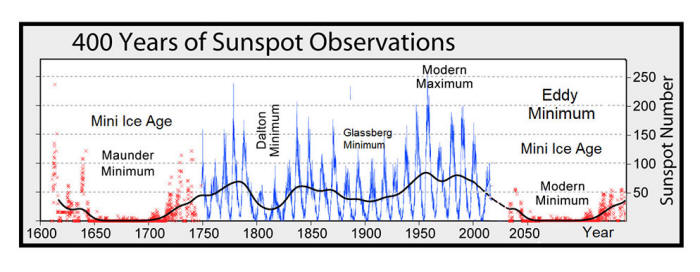
Unfortunately, those COLD TIMES appear to be returning - in line with, Even NASA appear to agree, if you read between the lines, with their forecast for this upcoming solar cycle (25) seeing it as "the weakest of the past 200 years," with the agency correlating previous solar shutdowns to prolonged periods of global cooling here.
Don't fall for bogus,
political agendas.
|