|
CHAPTER EIGHT
However, Eridu was not only the first city of the Sumerians, but also the first settlement of the Gods. Its name E.RI.DU echoed its earlier history, for it literally meant “Home in the Faraway Built”. a most appropriate name for the visitors from the planet Nibiru.
The Sumerian records state that Eridu belonged to the God Enki, who was placed in charge of Earth prior to the arrival of his brother Enlil.
The building of that first construction on Earth is commemorated in a Sumerian poem The Myth of Enki and Eridu:
Why then did the archaeologists not find any evidence of earlier inhabitation by the Gods? The simple explanation is that the earlier Eridu had been swept away by the Flood, and covered in a layer of mud so thick, that even if the archaeologists had known, it would have taken them a lifetime to excavate it.
As it was, nothing remained to suggest any earlier occupation of the site, so the spades were set aside at the level of the Sumerian Eridu, c. 3800 BC. The other sites of the Gods were similarly inundated by the Flood and buried in mud. How are we able to draw these conclusions?
In 1976, Zecharia Sitchin published a remarkable study, corroborating Sumerian claims that their cities had been built upon “the everlasting ground plan” of the Gods.’
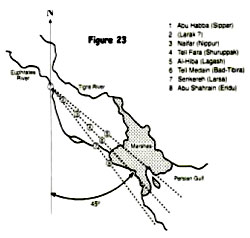
Sitchin realized that the locations of the ancient Sumerian cities did indeed follow a careful geographical plan, being equidistantly positioned on three lines, which converged at Sippar (Figure 23). Eridu itself was the most southerly city, situated close to the head of the Persian Gulf.
Whilst such a layout was clearly not beyond the Sumerians’ knowledge of geometry six thousand years ago, one key fact suggested a higher authority at work: the line through Bad-Tibira, Shuruppak, Nippur and Larak to Sippar intersected at exactly 45 degrees a meridian from the twin-peaked Mount Ararat, an outstanding landmark nearly 500 miles due north!
The full significance of the geometric plan
became clear when Zecharia Sitchin studied the meaning of the names
assigned to the cities. At the centre of the plan was Nippur, the
city of Enlil, chief of the Gods. Its Sumerian name was actually
NIBRU.KI, meaning the “Earth-Place of Nibiru”.
What about the other cities?
From all of these names, and the layout of the cities, Zecharia Sitchin concluded that, before the Flood, there had been a “triangular landing corridor” with a “spaceport” at Sippar and a “mission control” at Nippur.
Does this claim survive close scrutiny? It is difficult in retrospect for us to assess the suitability of this area for shuttle-type landings, since the debris from the Flood would have totally obscured the original landscape.
However, we do know that the area would have been rich in natural energy fuel, which seeped up through the ground even in Sumerian times. The idea that Sippar was an ancient space centre, where rockets ascended to “heaven”, is corroborated by its association with Utu/Shamash, for in later times he was well known as the God of the rockets.
Sitchin notes that, when Utu’s city was reconstructed at Sippar after the Flood, the Sumerian scribes reported a huge A.PIN inside his temple - an “Object that Ploughs Through”. This term appears to describe a modern rocket, possibly a museum piece to commemorate Sippar’s role as the first space centre.
If Zecharia
Sitchin is right, then the cities of Sumer were focussed in very
specific locations, in the southern part of Mesopotamia. Amazingly,
this happens to neatly solve one of the most intriguing questions
about the Sumerian civilization, because historians have always
wondered why northern Mesopotamia did not share in the early
blossoming of the south.
According to the Bible, this occurred on Mount Ararat, when Noah exited from the ark. His first action was to roast some animals as a sacrificial offering, and the Lord came down when he “smelled the pleasing aroma”. The Epic of Gilgamesh also states that the Gods “smelled the sweet savour” and “gathered like flies” for the feast.”
The story
hardly rings true, since Noah had just gone to great lengths to save
each species of animal, and anyway, how were the Gods supposed to
have landed an aircraft on the side of a mountain? An elapsed time
is therefore indicated, with the possibility that the feast took
place some time later, at a different location. The exact details of
how Noah and his family came from Ararat to their eventual lands
further south have not been explored, but in my view the answer may
well lie at the mysterious site of
Baalbek in Lebanon.
Whilst Baalbek’s earliest history remains unrecorded, its usage by aerial vehicles in Sumerian times has been clearly described in The Epic of Gilgamesh. The epic relates the adventures of Gilgamesh, a ruler of the Sumerian city of Uruk c. 2900 BC, and his friend Enkidu. Gilgamesh, who considered himself to be two thirds God, one third human, was preoccupied with death and the possibility of immortality. A large part of the tale describes his expedition to find the abode of the Gods in the “cedar mountain”. His aim is clear from his boast:
When Gilgamesh and his friend reached the cedar forests, they found it protected by an electrified fence. Enkidu opened his mouth and spoke, saying to Gilgamesh:
Taking heart, the heroic pair continued, until they found their way barred by a mechanical monster, Humbaba, whose “mouth is fire”, whose “breath is death”: They stood still and looked at the forest. They beheld the height of the cedar. They beheld the entrance to the forest. Where Humbaba was wont to walk there was a path; straight were the tracks and good was the passage. They beheld the mountain of the cedar, the dwelling place of the Gods, the throne-dais of Imini/Inanna.
Readers of the ancient epic have been left baffled as to why it was necessary to guard these cedars five thousand years ago, but the next quote makes it quite clear that it is an abode of the Gods, close to the cedar forest, which is being guarded. The nature of the Gods’ abode becomes clear when Gilgamesh is awoken from his sleep and says to Enkidu:
Shamash, the God of the rockets, then appeared on the scene, and assisted Gilgamesh in overcoming the mighty Humbaba. However, he was destined not to reach his goal beyond the cedar mountain.
In tablet VI of the epic, the Goddess Inanna attempted to seduce Gilgamesh; the latter, resisting her advances, recounted a long list of her former lovers. The adventure then ended with an irate Inanna chasing Gilgamesh and Enkidu back to the city of Uruk. The Epic of Gilgamesh not only confirms the use of Baalbek in Lebanon as a platform for aerial vehicles, but is consistent in all respects with our knowledge of the Sumerian Gods.
It ties in with Sumerian records that attribute the site to the God Ishkur (also known as Adad), since Utu/Shamash, the God of the rockets, was his son. The presence of Inanna is also to be expected, first because she was renowned as a flying Goddess, and secondly because she was the twin sister of Utu. Moreover, it is a fact that this triad of Ishkur, Utu and Inanna was worshipped for a millennia throughout the Near East, and the temples of Baalbek are still dedicated to them as Jupiter, Mercury and Venus respectively.
How then does Baalbek relate to the legend of Noah and the Flood? Despite the legend of the ark landing on Ararat, all of the scientific evidence and legends suggest that post-Flood agriculture began in the Bekaa valley where Baalbek is situated. This supports the theory that Baalbek survived the great Flood and became the site of safe haven for the returning Gods. How did Noah and his family make the trip from Ararat to the Bekaa valley?
One version of the Mount Ararat rendezvous places the Goddess Ishtar/Inanna at the scene. In the Babylonian version of The Epic of Gilgamesh, we find a remarkable parallel to the Biblical story of the rainbow and covenant with mankind. However, it is not the Lord, but the Goddess Ishtar who:
It may therefore have been Ishtar, in the course of surveying the flooded Earth, who was the first to spot the landed ark. Did she then bring Noah and his family safely back to Baalbek? An unusual tomb in a mosque at Karak Nuh, 20 miles south of Baalbek, is said to be the tomb of Noah (Plate 42).
A local legend relates that Noah was
extremely tall and could stand across the Bekaa valley, with one leg
on Mount Lebanon in the west and the other on the mountains of the
Anti-Lebanon in the east! According to this legend, it is one of
Noahs legs which is buried in the “tomb”, but the official line is
that it contains “merely a fragment of an ancient aqueduct”.” In
view of the legend, and Noah’s favoured position with the Gods, it
is quite possible that this unusually-shaped “tomb”, around sixty
feet long by a few feet wide, might contain a wing from an ancient
aircraft.
The Bible itself states that Noah was “a man of the soil.’ (a farmer), before he “planted a vineyard”. Professor Samuel Kramer also translated a Sumerian tablet which clearly identified the Lebanese mountains as the origin of post-Flood agriculture:
There is little doubt that Baalbek, and not Ararat, was the central
focus for Gods and men following the Flood.
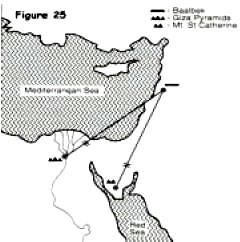
With hindsight it seems rather obvious, but, prior to Sitchin, no-one had ever noticed that the huge stone platform at Baalbek was equidistant from the pyramids at Giza and Mount St Catherine in the Sinai peninsula, as shown in (Figure 25).
What is the significance of Mount St Catherine? Apart
from the fact that it is one of the most sacred religious sites in
the world, it is, more importantly, the highest mountain in the
Sinai, at 8,700 feet above sea level.
The name of the mountain comes from the
martyrdom of
Catherine, who converted to Christianity, but was tortured and
beheaded in the early fourth century. Her body allegedly disappeared
and was found hundreds of years later by monks on the mountain which
now bears her name.
As described in chapter 4, the Giza pyramids were originally encased in polished white limestone casing blocks, which would have made them visible to the naked eye at a great distance.
Maurice Chatelain, a former NASA scientist who played a key role in the Apollo Moon projects, has observed that:
Maurice Chatelain calculated that the Pyramid would originally have been a radar reflector with a directivity factor of over 600 million for a 2 cm wave length, for example”. In layman’s language, that means an extremely powerful reflector!
Chatelain’s thoughts are echoed in the words of an ancient Sumerian poem, which appears to describe the Great Pyramid in a navigational role, “equipped” with a “pulsating beam” for “heaven to earth”:
As for the platform at Baalbek, the need for its huge stones (see chapter 3) can now be understood in the context of the immense weights and vertical forces which they had to withstand.
The textual
evidence, the geographical evidence and the physical evidence all
support each other to confirm that Baalbek was designed as a landing
platform for the rockets of the Gods.
Sitchin’s research of ancient texts indicated that repeated references to an E.KUR (“House like a Mountain”) were describing two separate places. One of these was quite clearly the ziggurat (step-pyramid) E.KUR of Enlil in Nippur. The other, however, was situated in the African lands of the Lower World.
The evidence is contained in an Akkadian text known as Ludlul Eel Nemeqi, which mentions an evil God who has “exited from the Ekur, across the horizon, in the Lower World”.
Can we confirm that the Lower World Ekur was indeed the Great Pyramid? A poem to the Goddess Ninharsag states so quite categorically:
Since the ziggurats in Mesopotamia had flat tops, only the Great Pyramid could possibly have fitted the description of a “pointed peak”. Furthermore, anyone who has stood in awe at the foot of the Pyramid would indeed describe it as a “House like a Mountain”.
The poem then continues to describe the Ekur with language that left Zecharia Sitchin in no doubt that it was accurately listing the Great Pyramid’s major features.
All in all, a perfect description of the
Great Pyramid’s interior!
As discussed in chapter 6, this battle resulted from the
occupation of Enljlite territories by the Egyptian God Seth and his
followers, fleeing from the vengeant Horus.
The bitter conflict which ensued reflected the tension between Enlil and Enki, and between their heirs Ninurta and Marduk, for control and supremacy over the Gods on Earth. The war sounds more like a rout. Supported by Adad (Ishkur) and Ishtar (Inanna), Ninurta used powerful weapons to destroy the settlements of Gods and men, and made the rivers run red with blood.
The texts
describe the retreat of the opposition into the mountain-lands of
Sinai and the land of Kush in present-day Sudan, where they were
pursued and crushed without mercy. “It was a ruthless campaign,
designed to remove human occupation from the lands of Sinai and to
send a clear message that the Near East would remain Enlilite
territory.
The peace conference is described in great detail in the text I Sing the Song of the Mother of the Gods.” What evidence exists to suggest that the war of the Gods as fact and not myth? One day, whilst reading the National Geographic, I came across a most unusual photograph of a mountain in Sudan. The mountain, Jebel Barkal, appeared to have been torn apart by a tremendous force, as can be seen in Plate 43.
Jebel Barkal is a strange and eerie mountain. It
rises 300 feet above the flat desert plain of the Sudan, a mile from
the Nile and close to Napata, the capital and sacred centre of
ancient Nubia (also known as the kingdom of Kush). The mountain
itself is regarded as especially sacred. At its base lies a ruined
temple complex revered as the southern abode of the Egyptian God,
Amen.
Kendall and his team found at the site a depiction of Amen actually seated inside the mountain. They declined to comment on the catastrophic event that had obviously ripped apart the mountain at its centre and blackened its interior.
But they did notice that the mountain had a “broad undulating top, which was carpeted with pebbles”.
These small blackened stones are a remnant of the powerful
explosion that once devastated this site.
The first clue is a mysterious well which has been excavated in the Great Pyramid’s Subterranean Chamber.
One Babylonian text confirms that this well was dug during the siege by Pa’s brother Nergal, in order to boost the Pyramid’s defenses:
After the surrender of the Enkiite Gods, the ancient texts describe how the victorious Ninurta entered the Ekur and disabled it.
A detailed description of his actions, deciphered by Zecharia Sitchin, provides further corroboration to identity the Ekur as the Great Pyramid and thus to authenticate the war of the Gods as a historic event.?
It is clear from the ancient text, known by its abbreviated name Lugal-e, that Ninurta was frustrated to see the conflict ended by peace settlement rather than a crushing defeat. He therefore vented his anger on the instruments left inside the Ekur. Inspecting its “stones” (crystals?), Ninurta determined their destiny - to be destroyed or taken away. In what was probably the Queen’s Chamber, he found the SHAM “Destiny” stone, which had a red glow.
Ninurta
ordered it to be dismantled and destroyed, claiming that the stone’s
powers had been used “to grab me to kill me, with a tracking which
kills to seize me. The stone is described in the poem to Ninharsag
as having “an outpouring like a lion, whom no-one dares attack”.
Today the enigmatic niche in the Queen’s Chamber stands empty, its
purpose otherwise unexplained.
On his return down the Grand Gallery, Ninurta
destroyed or removed, as appropriate, the multi-coloured “stones”
which created the rainbow-like effect. The text clearly names 22 of
these pairs of stones or crystals, whilst others are unfortunately
illegible. Today, there are 27 pairs of empty niches in the walls
above the ramps of the Grand Gallery and one further pair of empty
niches on the Great Step.
Thus did the era of the Great Pyramid come to an end. It was a fate which Ninharsag had anticipated as a necessary cost of securing the peace between the warring Gods.
In the Lugal-e text she exclaimed:
What was the chord-measuring function of the Great Pyramid, to which Ninharsag referred?
A chord is defined as a straight line connecting two points on a curved surface, such as the surface of the Earth. The line from the Great Pyramid to Baalbek was a chord which measured exactly the same as the chord from Mount St Catherine to Baalbek.
The unavoidable conclusion is that the pyramids were visual
markers for a pilot approaching towards Baalbek. but their role was
surely more than just passive radar reflectors. Somewhere inside the
Pyramid, the texts described a navigational beacon and/or radar
system which spread a “net” over heaven and Earth. Just as the
Sumerians claimed, it was indeed a House Like a Mountain “put
together for the shems”
Ereshkigal allotted to me the place-of-opening of the pilot-guiding instruments:
Geometry of the Gods
Baalbek had served its purpose following the Flood, but the Gods were now planning something more sophisticated. Whilst work was in progress, Baalbek continued as the central focus and a new beacon was established at Heliopolis, just 16 miles north-east of Giza.
The Heliopolis beacon was located in a position where it
could continue to be used after the completion of the new space
facilities, but in the meantime it was used to point the way to
Baalbek, and this necessitated another equidistant beacon site to be
temporarily set up on the eastern coast of the Sinai peninsula. It
is no coincidence that Heliopolis was once the most sacred city of
Egypt. where its earliest kings were consecrated.
The Greek-given name Heliopolis meant “City of the Sun”, a reference to the Sun God, Shamash. In so naming it, the Greeks recognised its original link with the other city of Heliopolis, also known as Baalbek. The original name of the Egyptian Heliopolis was Annu - a clear reference to the Sumerian AN, representing both “Heaven” and Anu, the heavenly father of the Gods.
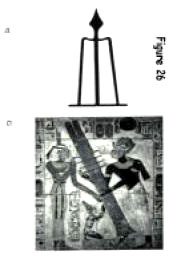
Several writers have noted that Annu meant “Pillar City”” and its hieroglyphic sign indeed resembled a high sloping tower (Figure 26a), sometimes surmounted by a mu or sky-chamber.
The original function of “Pillar City” may also shed light on the mysterious died symbol which is often associated with Heliopolis.
The Egyptologists usually refer to this strange object (shown in Figure 26b) as “the backbone of Osiris”, a meaningless expression of contrived symbolism. In fact, the djed symbol looks rather like a tower or lighthouse, and it was often depicted in pairs, sometimes in the mysterious Duat, flanking the Gateway to Heaven.
Did there once exist a second djed pillar with a similar
function? The second, temporary, flight path would suggest that such
a site must have once existed in the Sinai peninsula. It was almost
certainly for this reason that the Pyramid Texts referred to the
Heliopolitan Gods as the “Lords of the Dual Shrines”.
The new flight path was anchored on the two conical peaks of Mount Ararat - Little Ararat at a height of 13,000 feet and Great Ararat at 17,000 feet.
These two mountains are particularly distinctive.
Crowning a 25-mile wide massif, close to the Turkish-Iranian border,
they rise either side of a deep natural depression. Significantly,
the top few thousand feet of these peaks are permanently covered in
snow - an ideal visual marker for the pilots of the shems.
Actually, there is little difference
in height, Umm Shumar’s 8,500 feet being only slightly lower than St
Catherine. However, this deficit was more than offset by Mount Umm
Shumar’s brilliant natural prominence. Not only does it stand
separately from the surrounding mountains, but it also shines like a
beacon due to the presence of unusual mica particles in its rocks.
A study by Zecharia Sitchin noted that
Umm Shumar was in fact a mountain with three main peaks, and the
Sumerian names for the neighboring peaks provided the clues to
their function. One was named KA HARSAG, “The Gateway Peak”, and
another was named HARSAG ZALA.ZALAG, “Peak which Emits the
Brilliance”. No bets on which one contained the guidance equipment!
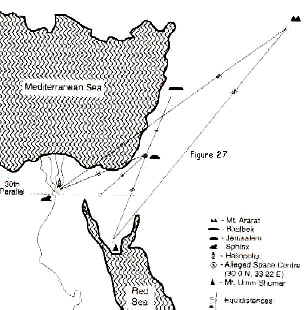
According to the geometrical plan, the space centre was built on the latitude line known as the thirtieth parallel north -a line which was symbolically important to the Gods. But where exactly on the thirtieth parallel? I decided to check for myself the geometry of the space centre, Heliopolis and Umm Shumar (and my readers are encouraged to get out their maps and rulers at this point).
I was able to pinpoint the site of the space centre alluded to by Zecharia Sitchin at a longitude of 33 degrees 22 minutes east, 122 miles equidistant from Heliopolis and Umm Shumar. The nearest modern town is Nakhl, which in ancient times was called El Paran.
The word Paran comes from a Hebrew root, meaning “abounding in caverns or caves”, an echo of the ancient Egyptian belief in the underground chambers of the Duat. Remarkably, as shown in Figure 27, the Gods found at Mount Zion, Jerusalem, a point that was exactly equidistant from the space centre and Baalbek (166 miles by my reckoning), and exactly equidistant from Umm Shumar and Heliopolis.
It was there, at Jerusalem, that the
mission control
centre was constructed. Bur before we study Jerusalem, let us first
follow the clues that identify the space centre in the Sinai.
From the granite mountains in the south to the limestone plateau in the centre, the landscape is a barren wilderness. However. despite the dry climate which makes the land unsuitable for farming, the Sinai occupies a strategic location, and has been a crossroads of world trade for thousands of years.
Not only does it provide the bridge from the continent of Africa to the continent of Asia, but it also provides a link from the Mediterranean Sea to the Red sea. Did a space centre of the Gods once exist in the central Sinai plain? Today there are no remains of such a site (for reasons which will be fully explained in chapter 10), but the uninterrupted 25-mile stretch between the Wadi El Agheidara and the Wadi el Natila would have presented an ideal hard, flat surface for landing shuttlecraft.
Although the Sinai is nowadays part of Egypt, the ancient chroniclers were in no doubt that it was previously a restricted area of the Gods. The best record of this fact is that of Gilgamesh, the Sumerian king who was obsessed with eternal life. Following his failed attempt to gain access to the platform at Baalbek, he made a second expedition to the Sinai.
His objective was to raise a shem and thereby gain immortality:
The route from Mesopotamia to Sinai is an indirect one, via the Dead Sea to the north, due to the mountains which protect the east flank of the Sinai peninsula. The Epic of Gilgamesh indeed described his route via a low-lying sea, where he asked a boatman named Urshanabi to ferry him across.
There is little doubt that these shallow waters were those now known as the Dead Sea, which The Epic of Gilgamesh refers to as the “sea of the waters of death”. Having crossed the sea, Gilgamesh eventually approached a mountain pass which was guarded by “Scorpion People”.
The mountain has a Sumerian name MA.SHU, meaning “Mount of the Supreme Barge”, which is identified in other texts as “Mount Most Supreme” and “the Place from which the Great Ones Ascend”:
Having sought the permission of Shamash, Gilgamesh was allowed to proceed to the place where Shamash raised his shems, but once again his quest was destined to fail, and the rest of the plot does not concern us here.
The question is whether we can confirm that Mount Mashu was a mountain in the Sinai. For the answer we have to cross the Sinai and study the Pyramid Texts of the ancient Egyptians.
The Pyramid Texts represent the religion of the pharaohs. They are essentially a statement of their obsessive belief in the afterlife, and in particular a place called the Duat.
The Duat is usually thought of as the realm of the dead king Osiris, a place in the starry skies where the dead pharaoh ascended to the afterlife. It’s purpose was clearly depicted by the hieroglyph of a star and falcon. Yet the pharaoh’s journey to the Duat was described in terms of a physical trip across land and water.
The journey, described in the Pyramid Texts, proceeded in an easterly direction; it began with a crossing over water (a lake of reeds with a divine ferryman) and proceeded over land between two mountains. At this point the pharaoh entered an “underworld”, where the “mouth” of the mountain was opened and the soul of the dead king rose to heaven. One Sumerian poem almost certainly refers to the same location as the “Mount of Howling Tunnels”.
The Egyptian journey eastward mirrored the journey of Gilgamesh westward the Sinai lying between. As Gilgamesh reached a mountain pass, so too did the dead pharaoh travel betweeI1 two mountains, for central Sinai is indeed surrounded by seven mountains and seven mountain passes. Their common destination was not a mythical underworld, but an underground space centre.
The journey to the Duat and thence to the stars was, for the Egyptians, simply an imitation of the journeys of their Gods - to Nibiru, Baalbek or wherever. It was thus associated with the perceived immortality of the Gods. The pyramids of Giza, and later Heliopolis were perceived as part of the gateway to the Duat and hence became a central part of the pharaohs afterlife cult.
The tale of the Duat sheds new light on the mysterious “opening of the mouth” ceremony performed on the dead pharaoh. And it also sheds light on the significance of the scarab beetle as a sacred Egyptian symbol of life and immortality the connection comes from that insect’s ability to burrow underground, and hence it was symbolically associated with the underground base in the Duat.
The textual clues to the past existence of a space centre in Sinai are completed by Zecharia Sitchin’s identification of Sinai as the legendary location of Tilmun (sometimes referred to as Dilmun). Scholars have usually located Tilmun in Bahrain, where an ancient trading post has indeed been discovered.
From a careful reading of the Sumerian texts, however, Sitchin concluded that there were in fact two Tilmuns - a Tilmun city and a Tilmun land. Furthermore, the search for the latter in the east was incorrect, since it was located not in the “land where the Sun rises" but in the land “where Shamash rises”.
Sitchin thus identified Tilmun land as the land of the Gods, a restricted zone that was set up after the Flood. Its name, in Sumerian, was TIL.MUN, meaning the “Land of the Missiles”.
A Sumerian poem entitled Enki and Ninharsag: a Paradise Myth, describes Tilmun land as a quiet, forsaken place, with words befitting of the Sinai desert:
The meaning of Tilmun is echoed by the name “Eagle Country”, by which Sinai later became known. The association of these fast, swooping birds with the Sinai and its space centre are highly revealing, since the Hebrew word for “eagle” (nesher) is associated with a “rushing sound” or a “gleaming flash”.
As noted in chapter 6, there is an important distinction between the shams, which flew in the Earth’s skies, and the “eagles”, which were rockets for ascending beyond Earth’s atmosphere.
There is little doubt that ancient references to eagles referred to the rockets of the Gods; in the Epic of Etana, for example, the Sumerian king Etana was carried aloft by an “eagle”, and he vividly described the Earth growing smaller and smaller until the oceans were the size of a “bread basket”.
Etana’s eagle (presumably its pilot) allegedly carried on
a conversation with him during the flight, a detail which can no
longer be dismissed as imaginative mythology.
Zecharia Sitchin has demonstrated that Ninharsag is the same Goddess as the Egyptian Hathor, who was also associated with Sinai. The name Hathor literally meant “She Whose Home is where the Falcons are”, a name which once again echoes the meaning of Tilmun. After the war of the Gods, the stewardship of the Sinai changed hands.
The intervention of Ninharsag to reprieve the besieged Enkiites had called her impartiality into question.
The Enlilites thus sought to bring the
Sinai, with its planned space facilities, firmly into their own
hands. The Sumerian poem I Sing the Song of the Mother of the Gods
describes the debate which led to the appointment of Nannar (a son
of Enlil and father of Utu/Shamash) in charge of Sinai.
And the main oasis town of Nakhl, in the central Sinai plain, also bears the name of Ningal in
the Semitic form of Nikhal. As for Ninharsag, her earlier
association of Sinai was not easily forgotten, and she continued to
be known as the “Lady of Sinai”.
Its most hallowed spot, Mount Moriah, is nowadays dominated by the Dome of the Rock, with its striking golden cupola, erected by the Muslims.
The “Rock” of Mount Moriah is in fact a large horizontal platform
known as Temple Mount. The Muslims identify it with El Aksn, the
location from which the prophet Muhammad was taken aloft by the
angel Gabriel through “seven heavens” to meet God.
It was also at this same, exact
location that the Lord directed Solomon to build the first “temple”
to the Lord 3,000 years ago. That temple was destroyed, rebuilt,
then destroyed again, and it is now marked by the site of the
Muslims’ golden cupola. What could possibly have triggered all of
these legends to be associated with Jerusalem, and why has it become
a place of such wide religious veneration?
This rock is believed to have magical powers and
has been regarded as sacred from ancient times. It is said that the
hidden parts of the rock contain unusual subterranean tunnels and
chambers. Modern legends speak of secret excavations connected with
the Knights Templar and the search for the holy Ark of the Covenant.
And finally, in the south, Mount Zion means literally the “Mount of the Signal”. The valleys around Jerusalem also provide significant clues: one valley is named in the Book of Isaiah as the Valley of Hizzayon, meaning the “Valley of Vision”. Another valley, Kidron, is named from a root word meaning “to glow, burn, radiate heat” and was thus known as the “Valley of Fire”.
Its lower course is today known as Wadi-en-Nar, or “Fire Wadi”.
The Valley of Hinnom, Geh Hinnorn in Hebrew, also has associations with fire, hence the Greek gehennu is usually translated as “hell”.’” According to legend, the Valley of Hinnom contains a doorway to an underworld, marked by a column of smoke rising between two palm trees.
Since time immemorial, Jerusalem has been an important and sacred site, but the official reason for this is rather obscure. Its importance cannot be traced to any advantage of geographic position. Nor was it important as a trade centre. In fact, it lay on the edge of a barren wilderness, and was quite remote from the major international trade routes.’” Its natural water supplies were limited, and yet its earliest inhabitants went to enormous trouble to construct unusually massive underground “water cisterns”.
Limited archaeological
explorations have identified 37 such cisterns with a total capacity
of about 10,000,000 gallons (37,850,000 liters). One cistern alone
was capable of holding approximately 2,000,000 gallons (7,570,000
liters) of water.
Put simply, from a conventional geographical perspective, Jerusalem’s location is a huge historical anomaly! If, however, we adopt a less conventional scientific approach, then the location of Jerusalem becomes immediately obvious. From the Gods’ perspective, the site would make an ideal mission control centre. The hostile environment mattered little, since staffing would be minimal.
The topography of the site was perfect - a small plateau,
surrounded by a steep valley on three sides
- defendable, should the need arise. And, finally, there were
several springs which allowed water to be produced and stored for
either industrial or space-related purposes.
Nothing whatsoever - he and his line of kings are a
historical blank. However, a clue to the meaning of the name
Melchizedek is supplied by Paul, who refers to him as “King of
Righteousness”. As we have seen, the Gods were called DIN.GIR for
which the first syllable meant “Pure” or “Righteous”. Thus
Melchizedek was almost certainly an Enlilite God.
I will say no more, other than to quote the non-biblical Book of Jubilees:
Clues from Jericho
As they sunk their trenches deep into the 70-feet high mound known as Telles Sultan, they found a lowest level with items dating to 8000 BC. This was an extraordinary find, for it occurred more than 4,000 years prior to the Sumerian civilization, at a time when man was thought to be living a simple, nomadic life.
Stranger still was the
fact that, from its earliest occupation, the site had been heavily
fortified. Among the archaeologists’ discoveries were a 30-feet high
stone tower with an internal staircase, city walls with heights up
to 20 feet, and an 8-feet deep ditch which extended over 20 feet
beyond the outer walls. These constructions were of high quality,
well-cut stones, fitted together without mortar.
The mystery is aptly summarized by one book which
refers to Jericho as “the intriguing missing link that still awaits
discovery”.
It therefore seems to have been a garrison to protect the eastern flank of the vital space facilities. As we have seen in The Epic of Gilgamesh, Jericho was indeed on the Dead Sea route which a land-based army would have to use to march on Jerusalem, or indeed to the space centre in the Sinai peninsula. As Zecharia Sitchin has pointed out, the original name of Jericho was Yeriho, literally meaning Moon City.
As the Moon is satellite to Earth, so too was Jericho the satellite and protector of Jerusalem, the navel of the Earth. A further ancient fortified site existed 12 miles north of Jerusalem. The modern town of Beitin marks the spot of ancient Beth-El, the “House of God”, where Jacob saw the angels of the Lord ascending and descending a stairway to heaven.
Half a mile to the east of Beitin, the site of
Borj Beitin is described as “one of the great viewpoints of
Palestine”, where the patriarch Abraham once pitched his tent.
Nearby, the modern village of Deir Diwan marks the site of the
ancient Ai, where excavations have dated the earliest levels to at
least 3000 BC. All of these sites stand on a stony plateau watered
by four springs - an ideal fortification post for Jerusalem’s
northern flank.
Zecharia Sitchin has concluded that Kadesh-Barnea in Sinai was the same town which the Akkadians had referred to as Dur-Mah-llani in Tilmun land. The name Dur-Mah-llani meant “the Great Fortified Place of the Gods”. Its location matches the place where Gilgamesh was forced to seek the permission of the “Scorpion People” to advance any further in his aim to raise a shem.
Biblical
scholars have always been mystified as to why a remote site in the
Sinai desert should have been the target for an invading force, but Sitchin’s explanation, in the context of a space centre in the
Sinai, provides a significant clue. In summary, it would seem that
the Gods’ space facilities were protected by a series of fortified
locations, all of which are otherwise quite baffling to scholars and
archaeologists.
With dimensions of 240 by 66 feet, the Sphinx (Plate 47) must surely qualify as the world’s greatest ever artistic achievement. In order to obtain these monumental dimensions, the sculptor has excavated thousands of tons of solid rock.
The experts
are unable to tell us what motivated the unknown artist, and they
have no clues, inscriptions or otherwise, to identify the date of
its creation. And yet, despite the lack of any evidence whatsoever,
the so-called experts are confidently able to tell us that the
Sphinx was carved by one or other of the builders of the three
nearby pyramids.
The
small size of the Sphinx’s head relative to its body may well
indicate that some significant re-profiling has taken place.
In addition, other representations of sphinxes. found in Egypt, combined the head of a ram with the body of a lion (plate 39) - not a Face of a pharaoh in sight! Furthermore, some commentators have expressed surprise that the concept of large-scale carving from solid rock was never emulated, despite its technical simplicity and plenty of suitable natural rock formations along the banks of the Nile.
It is these factors which have made the Sphinx such a mystery, for it appears totally distinct from the rest of ancient Egyptian culture. We have already identified the Giza pyramids as part of the Gods’ second flight path. Could the Sphinx also represent the handiwork of the Gods rather than man?
Like the pyramids, the Sphinx bears no
inscription. Its perfect art form, like the perfect 12-degree angle
of the Giza pyramids, was lever reproduced anywhere else. We should
not be surprised to find that these timeless monuments predate the
rule of the pharaohs in Egypt by thousands of years. In the case of
the Sphinx, this is now a scientific fact.
This erosion, according to the
science of geology. could only be the result of prolonged rainfall,
in contrast to the dry weather experienced in Egypt since 2500 BC.
Based on the climatic evidence, Schoch estimated that the Sphinx had
to be between 9,000 and 12,000 years old, when the climate in Egypt
was much wetter.
Zahi Hawass, the curator of the Sphinx and the pyramids, stated,
Once again. hard, factual evidence is swept under the carpet in order to maintain the paradigm and avoid a rewrite of the history books.
These skeptics should now reflect on the fact that the Sphinx faces eastwards exactly along the thirtieth parallel north towards the Sinai, corroborating the textual and geographical evidence that a space centre once existed at this same latitude. Did the Sphinx once bear the face of a God? It seems highly likely.
There is indeed a long-standing tradition
that the Sphinx bears the features of Hor-Akhiti the “Falcon of the
Horizon”, and one of the earliest Egyptian Gods, Ra, was known by
this name. It is surely no coincidence that the easterly horizon did
indeed mark the direction where the falcons landed.
|