|

by Adrian Norman
September 24, 2024
from
SCNR Website
Italian version
Karl F. Zeller and Ned Nikolov
IPCC Data shows
Human Activity Not Causing
Global Temperature Rises.
'These findings call for a fundamental reconsideration'
of the current man-made climate
change narrative
scientists say...
Data in a report from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate
Change (IPCC)
suggests that,
Earth's warming trend over the past two
decades may not be attributable to human-related activity.
Experts analyzing the report point to changes
in the planet's
albedo - the fraction of the Sun's energy
reflected by Earth - as the factor driving the rise in global
temperatures.
Albedo fluctuations have caused Earth to
reflect less solar energy and absorb more, leading to the warming
trend frequently cited by activists, advocates, and policymakers
focused on addressing climate change.
As
global "leaders" increasingly pursue aggressive policies to
mitigate climate change,
data suggesting human activity is
not the primary driver, could reshape public
policy worldwide...
In a recent interview with SCNR, Ned Nikolov,
Ph.D., a scientist specializing in climate, cosmology, and
astrophysics, expressed concerns about the integrity of IPCC
reports, accusing the panel of,
manipulating climate data.
Nikolov's research (Roles
of Earth's Albedo Variations and Top-of-the-Atmosphere Energy
Imbalance in Recent Warming), based on satellite data from
NASA's Clouds and the Earth's Radiant Energy System
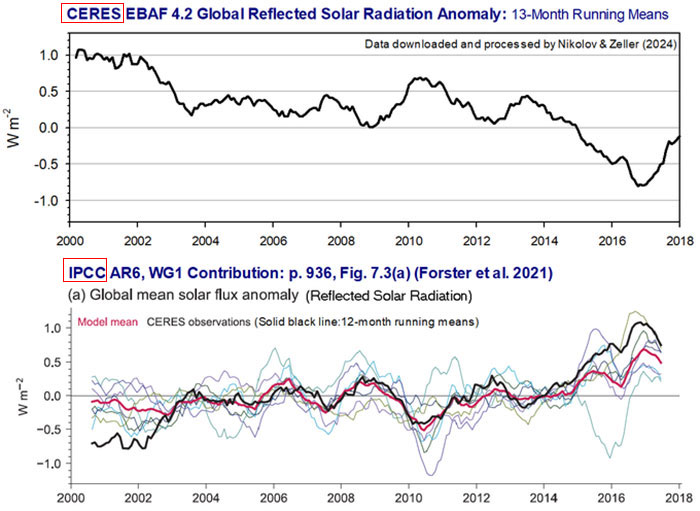
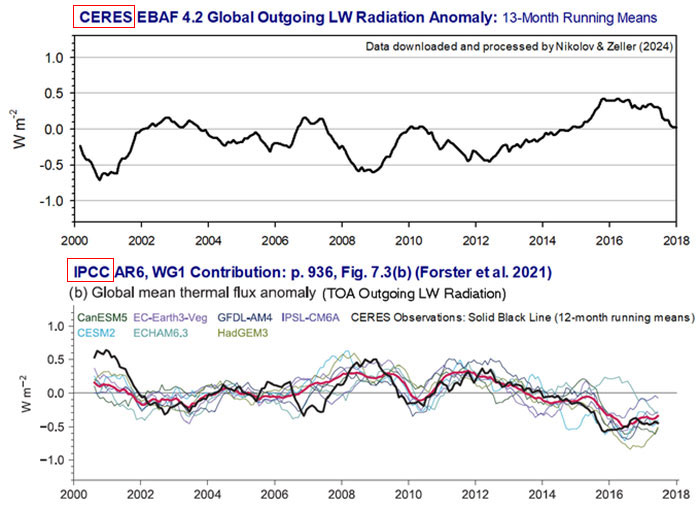
(CERES) project, reveals the IPCC misrepresented trends in solar and
long-wave radiation by inverting the data.
He argues that,
instead of accurately depicting that the
Earth is absorbing more solar energy due to reduced cloud cover
- an observation supported by NASA - the IPCC altered the data
to show the opposite, suggesting less absorbed solar energy.
Nikolov argues that this data inversion
is no accident and suggests that the IPCC may have
deliberately falsified this data to fit the widely accepted
narrative of man-made climate change.
The IPCC did not respond to multiple requests for comment...
Chapter 7 of WG1
Nikolov contends that all of the warming observed
in the past 24 years can be explained solely
by
increased solar energy absorption, not by rising CO2
levels or greenhouse gases.
"And this, this is not my theory," he
reiterated.
"It comes directly from satellite data that
NASA has provided. It's on their website."
He also pointed out broader implications for
climate science, asserting that
greenhouse gases like CO2
have,
a negligible effect on global warming
compared to the role of atmospheric pressure.
Karl Zeller, a climate scientist and
Nikolov's longtime research associate, criticized the IPCC's data
interpretation, noting that,
their models present misleading trends by
inverting the actual measurements, showing an increase in
albedo.
He told SCNR that these discrepancies arise from
how the IPCC calculates anomalies, which drastically changes the
findings.
The two scientists have developed a regression equation based on
satellite data that predicts temperature changes resulting from
variations in solar energy input.
Their research suggests that,
most recent warming can be attributed to
changes in solar radiation, not to
greenhouse gases, as is widely accepted.
They recently
published their findings in the peer-reviewed journal
Geomatics, concluding that the data,
"measured by CERES explain 100 percent of the
observed global warming trend and 83 percent of the interannual
GSAT variability over the past 24 years, including the extreme
2023 heat anomaly," which NASA
stated was the warmest year on
record.
"These findings call for a fundamental reconsideration of the
current paradigm of understanding about climate change and
related socio-economic initiatives aimed at drastic reductions
of industrial carbon emissions at all costs," they wrote.
Despite the significance of their conclusions,
Nikolov noted,
the lack of response from the broader
scientific community, attributing it to political and
financial interests that may hinder open discussion on
the issue.
He called for greater transparency and scrutiny
of climate data moving forward.
The pair's research highlights the potential collapse of the
"anthropogenic" global warming narrative if these discrepancies
are widely acknowledged.
But, Nikolov acknowledges the difficulty in challenging such a
deeply entrenched global consensus, as
most media outlets and
"scientific" institutions are reluctant to address these
findings...
|




